15. High Availability¶
15.1. High Availability of the Robin control plane¶
The Robin CNS management plane is comprised of services that manage the physical resources of a cluster and the applications deployed to the cluster. These management services don’t run directly on the host. Instead, they run in containers deployed on each node in the cluster. Several services are active on all nodes in the cluster, and there are control plane services that run inside pods on various nodes of the cluster. These services are responsible for handling the deployment of application resources on the node and for monitoring the health of the node.
Starting with Robin CNS v5.4.4, the Robin Control plane and data plane are separated. In the earlier architecture before Robin CNS v5.4.4, both the control plane and data plane are in a single Robin Pod.
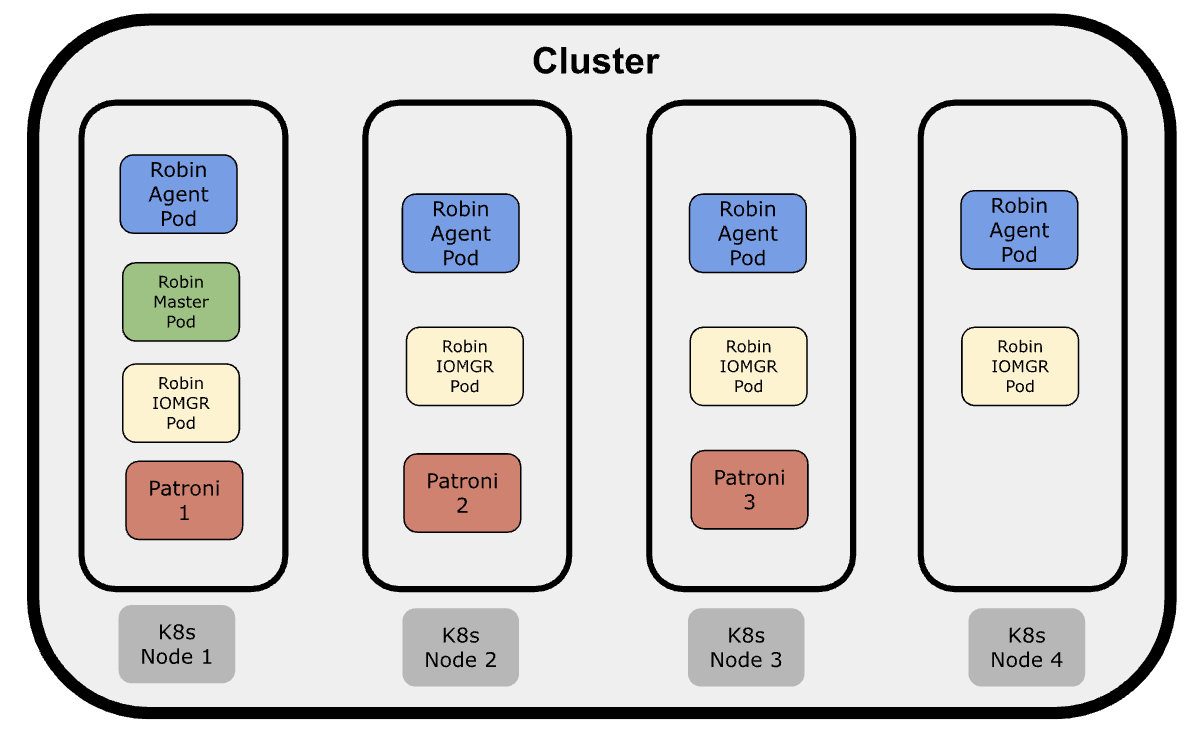
The following illustration explains the Robin CNS Architecture:
The following points explain the architecture:
The
robin-masterPods are deployed as a Deployment. Depending on the number of nodes in the cluster, therobin-masterPods can range from a minimum of one for a single-node cluster to a maximum of three.Note
If you utilize the
master_node_selectorparameter in therobin.yamlfile, you need to label the nodes where you want therobin-masterPods to be scheduled. The number ofrobin-masterPods will be scheduled on the designated nodes accordingly. For example, if a cluster has two nodes matching the master node selector, there will be two robin-master Pods deployed.If there are three replicas, only one of the
robin-masterPods plays the role of the Master role,and the remainingrobin-masterPods remain as Standby.Robin CNS utilizes the Kubernetes Lease mechanism to manage the master role. The
robin-masterlease is obtained on a first-come, first-served basis. Therobin-masterPod that secures the lease becomes the Master, while the remainingrobin-masterPods take on the role of Standby. If the node hosting therobin-master Pod(Master role) fails, one of the Standby Pods will acquire the lease and become the new Master. For more information on Kubernetes Lease mechanism, see, Lease Mechanism.The default lease duration and lease timeout for the
robin-masterPod are set to 15 seconds. Under normal conditions, therobin-masterPod renews the lease before it expires. If the lease is not renewed by the deadline, one of the Standby Pods will acquire the lease and assume the Master role. Note that if you have only onerobin-masterPod in the cluster, it fails over to any of the available nodes.The kubelet service, running on each node, monitors all containers deployed on that node. If any container fails, the kubelet will restart it. The
robinrcmcontainer within therobin-masterPod has a livenessProbe configured to run periodically. If this probe ever fails, the kubelet will restart therobinrcmcontainer.The
robin-masterPod runs the following master services:Consul Server
HTTPD
PHP and FPM
Robin Authentication server
Robin Bootstrap
Robin DB connect
Robin Event server
Robin Master
Robin Node monitor
Robin Server
Sherlock
Stormanager Server
The
robin-workerPods are deployed as a DaemonSet and therobin-workerPods run only the agent services, such asrobin-agentandmonitor-server. Therobin-iomgrPods are deployed as a DaemonSet and are responsible for handling I/O requests from the application.In Robin CNS v5.4.4 and later, Patroni is used as an independent PostgreSQL HA cluster, and it is deployed as part of Robin CNS installation. As the PostgreSQL HA is managed outside
robin-masterPods, its failover is not tied to Robin control-plane services failover.
A maximum of the three Patroni instances (Pods) are present in a cluster. The Patroni HA cluster has one leader (Leader), one synchronous replica (Sync Standby), and one asynchronous replica (Replica). All Patroni replicas are configured with permanent replication slots.
When there is a Google Anthos user cluster node pool of less than 3 nodes, Robin CNS installs a single replica Patroni cluster and brings up Robin CNS.
The Patroni cluster will automatically scale up when additional nodes are added to the node pool later. For example, when you install Robin CNS in a setup with two nodes from an Anthos User cluster, Robin CNS installs one Patroni instance, one
robin-masterPod, and two robin-agent Pods. When additional nodes are added to the cluster, the Patroni instances will scale up automatically to a maximum of three instances.The
/devbind mount from the host into Robin Pods is only needed forrobin-worker,robin-iomgr, andcsi-nodeplugin-robinPods.With control plane and data plane separation, master services will not have access to /dev.
The Robin master services provide access to user interfaces (UI/CLI/API) to CNS users. Due to this, no privileged Pod will take up any user APIs, reducing the attack surface significantly.
There are two replicas for the Robin CSI provisioner, attacher, resizer, and snapshotter Pods. Having two replicas reduces the time window of unavailability for CSI Pods if any node goes down.
15.2. Robin Patroni Monitor¶
The Robin Patroni Monitor feature monitors the status of the Patroni instances (Pods) in a cluster and provides events. The feature is automatically enabled on clusters running Robin CNS v5.4.10.
The Robin CNS architecture includes a highly available PostgreSQL cluster managed by Patroni, referred to as the Patroni Cluster.
To ensure high availability (HA), Patroni maintains three copies of its database, meaning a maximum of three Patroni instances (Pods) are present in a cluster at any given time.
The Patroni HA cluster consists of one Leader, one synchronous replica (Sync Standby), and one asynchronous replica (Replica). When the Leader Patroni instance goes down, the Sync Standby instance is promoted to become the new leader.
A Patroni cluster might become unavailable for a number of reasons. To monitor the status of the Patroni cluster, Robin CNS provides the Robin Patroni Monitor feature, which generates the events as required.
By default, the Robin Patroni Monitor feature is enabled, and it cannot be disabled.
15.2.1. View Status of Patroni cluster¶
You can view the status of the Patroni cluster, which displays the status of all three Patroni replicas. The Patroni replicas can have in one of the following statuses:
Ready
Not Ready
Failed
It also displays the status of the Robin Patroni Monitor feature. The Ready parameter always set to True because this feature is enabled by default.
Run the following command to view the status of the Patroni cluster:
# robin patroni status
--wide
--full
--json
|
Display additional attributes about the Patroni Cluster. |
|
Display all information about the Patroni Cluster. |
|
Output in JSON. |
Note
The patronictl list command also displays similar information about the Patroni cluster.
Example
# robin patroni status
Robin Patroni Monitor:
Deployment:
Deployed: True
Available: True
Ready: True
Pod:
Pod Deployed: True
Pod Status: Running
Robin Patroni Cluster:
Hostname | PodIP | Role | State | TL | Lag
----------------+---------------+--------------+-----------+----+-----
robin-patroni-0 | 192.0.2.190 | Sync Standby | streaming | 3 | 0
robin-patroni-1 | 192.0.2.180 | Replica | streaming | 3 | 0
robin-patroni-2 | 192.0.2.175 | Leader | running | 3 |
The following example is with the -- wide.
# robin patroni status --wide
Robin Patroni Monitor:
Deployment:
Deployed: True
Available: True
Ready: True
Pod:
Pod Deployed: True
Pod Status: Running
Robin Patroni Cluster:
Hostname | NodeName | HostIP | PodIP | WAL Offset | Role | State | TL | Lag
----------------+--------------+-------------+---------------+------------+--------------+-----------+----+-----
robin-patroni-0 | node-8-test | 192.0.2.192 | 192.169.3.190 | 0/8544178 | Sync Standby | streaming | 3 | 0
robin-patroni-1 | node-8-test1 | 192.0.2.198 | 192.169.4.4 | 0/8544178 | Replica | streaming | 3 | 0
robin-patroni-2 | node-8-test2 | 192.0.2.202 | 192.169.0.175 | 0/8544178 | Leader | running | 3 |
The following example is with the -- full.
# robin patroni status --full
Robin Patroni Monitor:
Deployment:
Deployed: True
Available: True
Ready: True
Pod:
Pod Deployed: True
Pod Status: Running
Robin Patroni Cluster:
Hostname | NodeName | HostIP | PodIP | WAL Offset | Role | State | TL | Lag
----------------+--------------+-------------+---------------+------------+--------------+-----------+----+-----
robin-patroni-0 | node-8-test | 192.0.2.192 | 192.169.3.190 | 0/85447A0 | Sync Standby | streaming | 3 | 0
DCS Last Seen: September 20, 2024 06:28:41
Location: 139741088
Replication State: streaming
Replayed Location: 139741088
Replayed WAL Offset: 0/85447A0
Hostname | NodeName | HostIP | PodIP | WAL Offset | Role | State | TL | Lag
----------------+--------------+-------------+-------------+------------+---------+-----------+----+-----
robin-patroni-1 | vnode-8-test1| 192.0.2.198 | 192.169.4.4 | 0/85447A0 | Replica | streaming | 3 | 0
DCS Last Seen: September 20, 2024 06:28:37
Location: 139741088
Replication State: streaming
Replayed Location: 139741088
Replayed WAL Offset: 0/85447A0
Hostname | NodeName | HostIP | PodIP | WAL Offset | Role | State | TL | Lag
----------------+--------------+-------------+---------------+------------+--------+---------+----+-----
robin-patroni-2 | vnode-8-test2| 192.0.2.202 | 192.169.0.175 | 0/85447A0 | Leader | running | 3 |
DCS Last Seen: September 20, 2024 06:28:37
Location: 139741088
15.2.2. View Events in robin-patroni-monitor Pod¶
You can view the Robin Patroni Monitor events in the robin-patroni-monitor Pod.
To view the events in the Patroni Pod, run the following command:
# kubectl logs --follow -n robinio <patroni Pod name>
Example
[robinds@cscale-82-61 ~]# kubectl logs --follow -n robinio robin-patroni-monitor-748b56476-7k5z7
{"zoneid": "1720063271", "type_id": 21002, "object_id": "robin-patroni-2", "timestamp": 1720655282.398766, "payload": {"description": "robin-patroni-2: State is 'stopped'"}, "level": "WARN"}
{"zoneid": "1720063271", "type_id": 21004, "object_id": "robin-patroni-2", "timestamp": 1720655297.6557193, "payload": {"description": "robin-patroni-2: State is 'running'"}, "level": "INFO"}
{"zoneid": "1720063271", "type_id": 21001, "object_id": "robin-patroni-1", "timestamp": 1720655521.8451483, "payload": {"description": "robin-patroni-1: Promoted to Leader (master)"}, "level": "INFO"}
{"zoneid": "1720063271", "type_id": 21002, "object_id": "robin-patroni-0", "timestamp": 1720655577.8727887, "payload": {"description": "robin-patroni-0: State is 'stopped'"}, "level": "WARN"}
{"zoneid": "1720063271", "type_id": 21003, "object_id": "robin-patroni-0", "timestamp": 1720655638.9599402, "payload": {"description": "robin-patroni-0: State is 'stopped'"}, "level": "ERROR"}
{"zoneid": "1720063271", "type_id": 21004, "object_id": "robin-patroni-0", "timestamp": 1720655664.435924, "payload": {"description": "robin-patroni-0: State is 'running'"}, "level": "INFO"}
15.2.3. Patroni Events¶
The Robin Patroni Monitor feature generates the following Event types to the robin-patroni-monitor Pod logs if there are any change in status the Patroni replicas:
You can view the events by running the robin event-type list command. For more information, see Listing event types.
Event type |
Level |
Description |
|---|---|---|
EVENT_PATRONI_LEADER_CHANGE |
INFO |
The event is generated when there is a change in Leader role in the Patroni cluster. |
EVENT_PATRONI_INSTANCE_NOT_READY |
WARN |
The event is generated when any of the replicas in the Paroni cluster are in the NotReady status. |
EVENT_PATRONI_INSTANCE_FAILED |
ERROR |
The event is generated when any of the Patroni replicas are in the Failed status. |
EVENT_PATRONI_INSTANCE_READY |
INFO |
The event is generated when any of the Patroni replicas moved to the Ready status. |
15.3. Robin Manager¶
A node running Master Pod acts a Manager.
The following commands are described in this section:
|
View robin manager list and services |
15.3.1. Viewing Manager Details¶
You can view the manager details by running the following command:
# robin manager <history> <list>
|
Displays all master failover events |
|
Displays list of managers |
15.3.1.1. View Manager Histroy¶
Run the following command to view Robin manager history.
# robin manager <history>
Example
root@eqx04-flash06:~# robin manager history
+---------------------------------+----------------------------+
| Hostname | Start Time |
+---------------------------------+----------------------------+
| hypervvm-72-42.robinsystems.com | 2023-09-06 20:44:58.523284 |
+---------------------------------+----------------------------+
15.3.1.2. View Manager List¶
Run the following command to view Robin manager list and services status.
robin manager list --services
--all
|
Displays services status info for manager |
|
Displays all PODs and status |
Example:
root@eqx04-flash06:~# robin manager list --services
+-----------------------------------+-------+------+------+------+----------+------+---------+-------+-------+
| Hostname | ConSr | RSer | REvt | RAer | Sherlock | NMon | Stormgr | PGSQL | Httpd |
+-----------------------------------+-------+------+------+------+----------+------+---------+-------+-------+
| master.robin-server.service.robin | UP | UP | UP | UP | UP | UP | UP | UP | UP |
+-----------------------------------+-------+------+------+------+----------+------+---------+-------+-------+
UP: Running
PARTIAL: Partially Running
UNKNOWN: Not Managed
CRIT: Critical and Down
DOWN: Not Running
root@eqx04-flash06:~# robin manager list --all
+-----------------------------------+--------------+---------------+---------------+--------------+---------+
| Hostname | Service IP | POD IP | Node | Node IP | Status |
+-----------------------------------+--------------+---------------+---------------+--------------+---------+
| master.robin-server.service.robin | 10.107.24.37 | 192.180.2.250 | eqx03-flash06 | 10.9.140.106 | Running |
+-----------------------------------+--------------+---------------+---------------+--------------+---------+